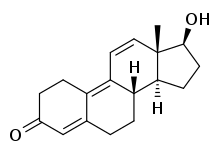
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Trienolone; Trienbolone; RU-2341; Δ9,11-Nandrolone; 19-Nor-δ9,11-testosterone; Estra-4,9,11-trien-17β-ol-3-one |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection (as esters) |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Progestogen |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Intramuscular: 100% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 6-8 hours |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.127.177 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H22O2 |
| Molar mass | 270.372 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Trenbolone is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) of the nandrolone group which itself was never marketed.[2][3][4][5][6] Trenbolone ester prodrugs, including trenbolone acetate (brand names Finajet, Finaplix, others) and trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate (brand names Parabolan, Hexabolan), are or have been marketed for veterinary and clinical use.[2][3][4][6][7][8] Trenbolone acetate is used in veterinary medicine in livestock to increase muscle growth and appetite, while trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate was formerly used clinically in humans but is now no longer marketed.[2][3][4][6] In addition, although it is not approved for clinical or veterinary use, trenbolone enanthate is sometimes sold on the black market under the nickname Trenabol.[6]
Uses
Veterinary
Trenbolone, as trenbolone acetate, improves muscle mass, feed efficiency, and mineral absorption in cattle.[6]
Side effects
Sometimes human users may experience an event called "tren cough" shortly after or during an injection, where the user experiences a violent and extreme coughing fit, which can last for minutes.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Trenbolone has both anabolic and androgenic effects.[6] Once metabolized, trenbolone esters have the effect of increasing ammonium ion uptake by muscles, leading to an increase in the rate of protein synthesis. It may also have the secondary effects of stimulating appetite and decreasing the rate of catabolism, as all anabolic steroids are believed to; however, catabolism likely increases significantly once the steroid is no longer taken.[9] At least one study in rats has shown trenbolone to cause gene expression of the androgen receptor (AR) at least as potent as dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This evidence tends to indicate trenbolone can cause an increase in male secondary sex characteristics without the need to convert to a more potent androgen in the body.[10]
Studies on metabolism are mixed, with some studies showing that it is metabolized by aromatase or 5α-reductase into estrogenic compounds, or into 5α-reduced androgenic compounds, respectively.[11][12]
Trenbolone has potency five times as high as that of testosterone.[6][13] Trenbolone also binds with high affinity to the progesterone receptor,[6][13][14][15] Trenbolone binds to the glucocorticoid receptor, as well.[14]
Pharmacokinetics
To prolong its elimination half-life, trenbolone is administered as a prodrug as an ester conjugate such as trenbolone acetate, trenbolone enanthate, or trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate.[2][3][4][6] Plasma lipases then cleave the ester group in the bloodstream leaving free trenbolone.
Trenbolone and 17-epitrenbolone are both excreted in urine as conjugates that can be hydrolyzed with beta-glucuronidase.[16] This implies that trenbolone leaves the body as beta-glucuronides or sulfates.
Chemistry
Trenbolone, also known as 19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone or as estra-4,9,11-trien-17β-ol-3-one, is a synthetic estrane steroid and a derivative of nandrolone (19-nortestosterone).[2][3][6] It is specifically nandrolone with two additional double bonds in the steroid nucleus.[2][3][6] Trenbolone esters, which have an ester at the C17β position, include trenbolone acetate, trenbolone enanthate, trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate, and trenbolone undecanoate.[2][3][6][17]
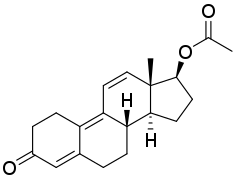
| Name: | Trenbolone | Trenbolone acetate | Trenbolone enanthate | Trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate
(cyclohexylmethylcarbonate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structural[17] |  |
 |
 |
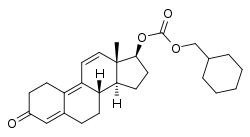 |
| Formula | C18H22O2 | C20H24O3 | C25H34O3 | C26H34O4 |
| Crystal system[17] | monocrystalic | monocrystalic | monocrystalic | |
| Elimination half life | 48–72 hours | short | long
11 days[17] |
8 days[17] |
History
Trenbolone was first synthesized in 1963.[19]
Society and culture
Generic names
Trenbolone is the generic name of the drug and its INN and BAN.[2][3][4] It has also been referred to as trienolone or trienbolone or tren.[2][3][4][20]
Legal status
Some bodybuilders and athletes use trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate and other esters (acetate, enanthate) for their muscle-building and otherwise performance-enhancing effects.[21][6] Such use is illegal in the United States and several European and Asian countries. The DEA classifies trenbolone and its esters as Schedule III controlled substances under the Controlled Substances Act.[22] Trenbolone is classified as a Schedule 4 drug in Canada[23] and a class C drug with no penalty for personal use or possession in the United Kingdom.[24] Use or possession of steroids without a prescription is a crime in Australia.[25]
Doping in sports
There are known cases of doping in sports with trenbolone esters by professional athletes.
See also
References
- ↑ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-15.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. p. 1591. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Morton IK, Hall JM (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 279–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ↑ "Trenbolone".
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Llewellyn W (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 491–499, 618–, 724–. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.
- ↑ Nichols W, Hutcheson J, Streeter M, Corrigan M, Nuttelman B. "Implant Strategies for Finishing Cattle using Revalor® (trenbolone acetate and estradiol), Finaplix® (trenbolone) and/or Ralgro® (zeranol)" (PDF). Merck Animal Health.
- ↑ Kicman AT (June 2008). "Pharmacology of anabolic steroids". British Journal of Pharmacology. 154 (3): 502–521. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.165. PMC 2439524. PMID 18500378.
- ↑ Fahey TD (March 1998). "Anabolic Steroids: Mechanisms and Effects". Encyclopedia of sports medicine and science. Internet Society for Sport Science.
- ↑ Wilson VS, Lambright C, Ostby J, Gray LE (December 2002). "In vitro and in vivo effects of 17beta-trenbolone: a feedlot effluent contaminant". Toxicological Sciences. 70 (2): 202–211. doi:10.1093/toxsci/70.2.202. PMID 12441365.
- ↑ Yarrow JF, McCoy SC, Borst SE (June 2010). "Tissue selectivity and potential clinical applications of trenbolone (17beta-hydroxyestra-4,9,11-trien-3-one): A potent anabolic steroid with reduced androgenic and estrogenic activity". Steroids. 75 (6): 377–389. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2010.01.019. PMID 20138077. S2CID 205253265.
- ↑ Gettys TW, D'Occhio MJ, Henricks DM, Schanbacher BD (January 1984). "Suppression of LH secretion by oestradiol, dihydrotestosterone and trenbolone acetate in the acutely castrated bull". The Journal of Endocrinology. 100 (1): 107–112. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1000107. PMID 6361192.
- 1 2 Nicholas Mascie-Taylor CG, Rosetta L (13 January 2011). Reproduction and Adaptation: Topics in Human Reproductive Ecology. Cambridge University Press. pp. 69–. ISBN 978-1-139-49430-4.
- 1 2 APMIS.: Supplementum. Munksgaard. 2001. p. 5339. ISBN 9788716164575.
- ↑ McKerns KW (13 March 2013). Reproductive Processes and Contraception. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 171–. ISBN 978-1-4684-3824-6.
- ↑ Schänzer W (July 1996). "Metabolism of anabolic androgenic steroids". Clinical Chemistry. 42 (7): 1001–1020. doi:10.1093/clinchem/42.7.1001. PMID 8674183.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Borodi G, Turza A, Camarasan PA, Ulici A (2020). "Structural studies of Trenbolone, Trenbolone Acetate, Hexahydrobenzylcarbonate and Enanthate esters". Journal of Molecular Structure. 1212: 128127. Bibcode:2020JMoSt121228127B. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128127. ISSN 0022-2860. S2CID 216299984.
- ↑ Ruiz P, Strain EC (2011). Lowinson and Ruiz's Substance Abuse: A Comprehensive Textbook. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-1-60547-277-5.
- ↑ Schänzer W (July 1996). "Metabolism of anabolic androgenic steroids". Clinical Chemistry. 42 (7): 1001–1020. doi:10.1093/clinchem/42.7.1001. PMID 8674183.
- ↑ Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (1990). Residues of Some Veterinary Drugs in Animals and Foods: Monographs Prepared by the Thirty-Fourth Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives, Geneva, 30 January-8 February 1989. Food & Agriculture Org. pp. 88–. ISBN 978-92-5-102933-6.
- ↑ "Trenbolone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate use in bodybuilding". 20 November 2021.
- ↑ "Controlled Substances Act". United States Food and Drug Administration. 11 June 2009. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ↑ "Controlled Drugs and Substances Act". laws-lois.justice.gc.ca. Archived from the original on 2012-09-15.
- ↑ "Consideration of the Anabolic Steroids". London: Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs. September 2010. Archived from the original on 2011-09-22.
- ↑ "Australian Institute of Criminology - Steroids". Archived from the original on 2012-03-23. Retrieved 2011-08-22.
Further reading
- Meyer HH (January 2001). "Biochemistry and physiology of anabolic hormones used for improvement of meat production". APMIS. 109 (1): S336–S344. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0463.2001.tb05785.x. PMID 11297191. S2CID 23149070.
- Yarrow JF, McCoy SC, Borst SE (June 2010). "Tissue selectivity and potential clinical applications of trenbolone (17beta-hydroxyestra-4,9,11-trien-3-one): A potent anabolic steroid with reduced androgenic and estrogenic activity". Steroids. 75 (6): 377–389. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2010.01.019. PMID 20138077. S2CID 205253265.