 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
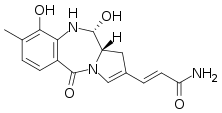
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-3-[(11S,11aS)-9,11-Dihydroxy-8-methyl-5-oxo-5,10,11,11a-tetrahydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,1-c] [1,4]benzodiazepin-2-yl]prop-2-enamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H17N3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 315.329 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Anthramycin is a pyrrolobenzodiazepine antibiotic with antitumor activity.[1] First derived from the thermophilic actinomycete Streptomyces refuineus by M. D. Tendler and S Korman in the 1950s, it was first successfully synthesized in a laboratory setting by Leimgruber et al. in 1965. Due to the unstable nature of the chemical structure, characterization of the species was done on its epimer, anthrmycin-11-methyl-ether. This derivative can be formed by recrystallization of anthramycin from hot methanol.
Chemical structure
The chemical structure of anthramycin was first elucidated by Leimgruber using nuclear magnetic resonance and ultraviolet spectroscopy. Using another similarly structured fermentation product simply referred to as 'yellow pigment' as a basis of comparison, he was able to identify all major functional groups of the structure. The structure of the species was narrowed down to one of two possible candidates: one with a pyrrolobenzodiazepine nucleus, and another with a pyridoquinazoline skeleton. The first structure was confirmed through the use of mass spectrometry.
Medical uses
Anthramycin is an active anti-tumor agent and antibiotic.[2] It works by inhibiting the synthesis of RNA and DNA of carcinoma cells. It is a competitive inhibitor of cell-free RNA and DNA synthesis, and blocks the action of DNase I. Anthramycin-methyl-ether (AME) forms a complex with DNA which blocks off synthesis by prohibiting DNA binding with proper enzymes. The species is heavily cytotoxic. Anthramycin has been shown particularly effective against sarcomas, lymphomas, and gastrointestinal neoplasms.
Side effects
Use of anthramycin has been largely limited due to a cardiotoxicity so high that it limits dosing. Acute tissue necrosis has also been noted at the injection site of the antibiotic, and side effect of its high cytotoxicity. Repeated injections in mice have been shown to adversely affect mitochondrial metabolism. The mice also showed abnormal electrocardiograms. As such, the side effects of such medication may outweigh the benefits. Alternatives such as doxorubicin are today more widely available and prescribed, due to more mild side effects along with increased anti-tumor action.
See also
References
- ↑ Kitamura, Tsuyoshi; Yoshihiro Sato; Miwako Mori (2004). "Synthetic study of (+)-anthramycin using ring-closing enyne metathesis and cross-metathesis". Tetrahedron. 60 (43): 9649–57. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2004.07.040.
- ↑ Sartorelli, Alan C.; Johns, David G. (27 November 2013). Antineoplastic and Immunosuppressive Agents. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 647. ISBN 9783642658068. Retrieved 1 November 2016.