| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H17ClN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 328.79 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Girisopam[1] (GYKI-51189, EGIS-5810) is a drug which is a 2,3-benzodiazepine derivative, related to tofisopam[2] and zometapine. It has selective anxiolytic action with no sedative, anticonvulsant or muscle relaxant effects.[2][3][4]
Synthesis
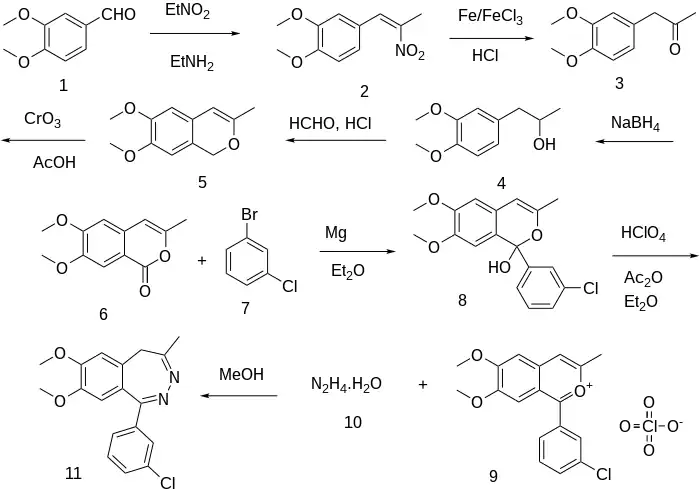
Henry reaction between Veratraldehyde [120-14-9] (1) and nitroethane gives 1,2-Dimethoxy-4-(2-nitropropenyl)benzene [122-47-4] (2). Treatment with iron and muriatic acid in the presence of iron trichloride catalyst gives 3,4-Dimethoxyphenylacetone [776-99-8] (3). The reduction of the ketone with sodium borohydride gives 1-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-2-propanol [19578-92-8] (4). Treatment with formaldehyde in acid gives 6,7-dimethoxy-3-methyl-1H-isochromene, CID:57074411 (5). Oxidation by chromium trichloride gives 3-Methyl-6,7-Dimethoxyisocoumarin, CID:12349213 (6). Grignard reaction with 1-Bromo-3-Chlorobenzene [108-37-2] (7) gives (8). Treatment with Perchloric acid leads to 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-3-methyl 6,7-dimethoxy-2-benzopyrylium perchlorate CID:14502385 (9).
Ex 39: The reaction between (9) and hydrazine hydrate (10) in methanol solvent gives girisopam (11).
See also
References
- ↑ US 4322346, Korosi J, Lang T, Szekely J, Andrasi F, Zolyomi G, Borsi J, Katali G, Hamori T, Gabriella S, Zsuz MN, Miglecz E, "5H-2,3-Benzodiazepine derivatives", issued 30 March 1982
- 1 2 Andrási F, Horváth K, Sineger E, Berzsenyi P, Borsy J, Kenessey A, Tarr M, Láng T, Kórösi J, Hámori T (October 1987). "Neuropharmacology of a new psychotropic 2,3-benzodiazepine". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 37 (10): 1119–24. PMID 2893623.
- ↑ Horváth K, Andrási F, Botka P, Hámori T (1992). "Anxiolytic profile of girisopam and GYKI 52,322 (EGIS 6775). Comparison with chlordiazepoxide and buspirone". Acta Physiologica Hungarica. 79 (2): 153–61. PMID 1363928.
- ↑ Horváth EJ, Salamon C, Bakonyi A, Fekete MI, Palkovits M (July 1999). "[(3)H]-girisopam, a novel selective benzodiazepine for the 2, 3-benzodiazepine binding site". Brain Research. Brain Research Protocols. 4 (2): 230–5. doi:10.1016/s1385-299x(99)00025-2. PMID 10446419.
- ↑ Jeno Korosi, et al. U.S. Patent 4,322,346 (1982 to Egyt Gyogyszervegyeszeti Gyar).
- ↑ Bhide, B. H., Brahmbhatt, D. I. (December 1980). "Isocoumarins: Part 4. Synthesis of 5,6-dimethoxy, 6,7-dimethoxy, 7,8-dimethoxy, 5,7-dimethoxy, 5,8-dimethoxy-3-methyl-isocoumarins and a new synthesis of (±)-6-methoxy mellein". Proceedings / Indian Academy of Sciences. 89 (6): 525–532. doi:10.1007/BF02881086.
- ↑ Black, ed. (2005). Category 2, Hetarenes and Related Ring Systems: Six-Membered Hetarenes with One Nitrogen or Phosphorus Atom. Georg Thieme Verlag. doi:10.1055/b-003-121804.
- ↑ Shriner, R. L., Johnston, H. W., Kaslow, C. E. (March 1949). "ISOBENZOPYRYLIUM SALTS. I. PREPARATION AND REACTIONS OF 1-PHENYL-2-BENZOPYRYLIUM SALTS 1". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 14 (2): 204–209. doi:10.1021/jo01154a003.
- ↑ Thomas, E. J., ed. (2003). Category 2, Hetarenes and Related Ring Systems: Six-Membered Hetarenes with One Chalcogen. Georg Thieme Verlag. doi:10.1055/b-003-121801.