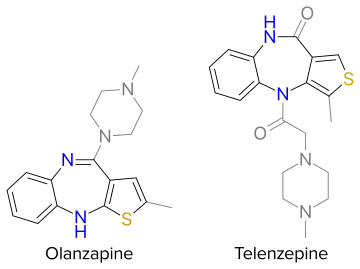
General structure of thienobenzodiazepines. Core is highlighted by black and color. Grey depicts accessory functional groups.
Thienobenzodiazepine is a heterocyclic compound containing a diazepine ring fused to a thiophene ring and a benzene ring. Thienobenzodiazepine forms the central core of pharmaceutical drugs including atypical antipsychotic olanzapine (Zyprexa) and antimuscarinic telenzepine. Thienobenzodiazepines act relatively selectively at the α2 subunit of the GABAA receptor.[1]
References
- ↑ Bymaster, Frank P; Calligaro, David O; Falcone, Julie F; Marsh, Richard D; Moore, Nicholas A; Tye, Nicholas C; Seeman, Philip; Wong, David T (February 1996). "Radioreceptor Binding Profile of the Atypical Antipsychotic Olanzapine". Neuropsychopharmacology. 4 (2): 87–96 – via PubMed.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.