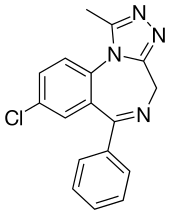
Chemical structure of alprazolam, a common triazolobenzodiazepine
Triazolobenzodiazepines (TBZD) are a class of benzodiazepine (BZD) derivative pharmaceutical drugs. Chemically, they differ from other benzodiazepines by having an additional triazole ring fused to the diazepine ring. The triazole and diazepine rings share a nitrogen atom.
Examples include:
Synthesis
Synthesis of 1-methyltriazolobenzodiazepines (alprazolam type) is possible by heating 1,4-benzodiazepin-2-thiones with hydrazine and acetic acid in n-butanol under reflux.[1]
References
- ↑ Hester JB, Duchamp DJ, Chidester CG (1971): "A synthetic approach to new 1,4-benzodiazepine derivatives." Tetrahedron Letters, Vol. 12, pp. 1609-1612.
External links
 Media related to Triazolobenzodiazepines at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Triazolobenzodiazepines at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.