 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | α-Hydroxyetizolam |
| Dependence liability | Moderate |
| Routes of administration | Oral, sublingual, rectal |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 8.2 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
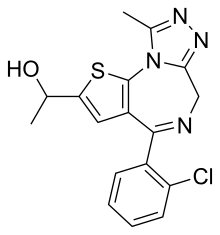
| Formula | C17H15ClN4OS |
| Molar mass | 358.84 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
α-Hydroxyetizolam is the pharmacologically active metabolite of etizolam.[2] α-Hydroxyetizolam has a half-life of approximately 8.2 hours.[3]
Etizolam's other non-pharmacologically active metabolite in humans is 8-hydroxyetizolam.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Fracasso C, Confalonieri S, Garattini S, Caccia S (1991-02-01). "Single and multiple dose pharmacokinetics of etizolam in healthy subjects". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 40 (2): 181–185. doi:10.1007/BF00280074. PMID 2065698. S2CID 10176681.
- 1 2 "alpha-Hydroxyetizolam". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 2021-02-23.
- ↑ Nakamae T, Shinozuka T, Sasaki C, Ogamo A, Murakami-Hashimoto C, Irie W, et al. (November 2008). "Case report: Etizolam and its major metabolites in two unnatural death cases". Forensic Science International. 182 (1–3): e1-6. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2008.08.012. PMID 18976871.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.