 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
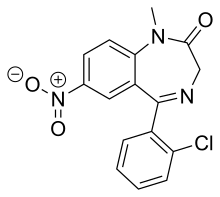
| Formula | C16H12ClN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 329.74 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Ro05-4082 (N-methylclonazepam, ID-690) is a benzodiazepine derivative developed in the 1970s. It has sedative and hypnotic properties, and has around the same potency as clonazepam itself.[1] It was never introduced into clinical use. It is a structural isomer of meclonazepam (3-methylclonazepam), and similarly has been sold as a designer drug, first being identified in Sweden in 2017.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Fukuda H, Kudo Y, Ono H, Togari A, Tanaka Y (January 1977). "[Pharmacological study on 5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-7-nitro-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one (ID-690), with special reference to the effects on motor systems]". Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. Folia Pharmacologica Japonica (in Japanese). 73 (1): 123–34. doi:10.1254/fpj.73.123. PMID 558942.
- ↑ "Novel Benzodiazepines. A review of the evidence of use and harms of Novel Benzodiazepines" (PDF). Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs. April 2020.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.