Collioure
Cotlliure | |
|---|---|
 The Church of Our Lady of the Angels in Collioure | |
.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms | |
Location of Collioure | |
 Collioure  Collioure | |
| Coordinates: 42°31′36″N 3°04′53″E / 42.5267°N 3.0814°E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Occitania |
| Department | Pyrénées-Orientales |
| Arrondissement | Céret |
| Canton | La Côte Vermeille |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2026) | Guy Llobet[1] |
| Area 1 | 13.02 km2 (5.03 sq mi) |
| Population | 2,517 |
| • Density | 190/km2 (500/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 66053 /66190 |
| Elevation | 0–655 m (0–2,149 ft) (avg. 10 m or 33 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Collioure (French pronunciation: [kɔljuʁ] ⓘ; Catalan: Cotlliure, IPA: [kuˈʎːiwɾə]) is a commune in the southern French department of Pyrénées-Orientales.[3]
Geography
The town of Collioure is on the Côte Vermeille (Vermilion Coast), in the canton of La Côte Vermeille and in the arrondissement of Céret.
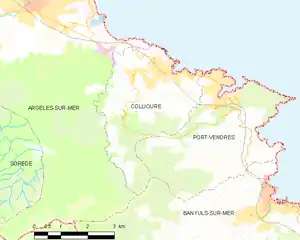
Toponymy
History
There is a record of the castle at "Castrum Caucoliberi" having been mentioned as early as 673, indicating that the settlement here was of strategic and commercial importance during the Visigoth ascendancy.
Collioure used to be divided into two villages separated by the river Douy, the old town to the south named Port d'Avall (in French known as Le Faubourg) and the upstream port, Port d'Amunt (in French known as Le Mouré).
Collioure was taken in 1642 by the French troops of Maréchal de la Meilleraye. A decade later, the town was officially surrendered to France by the 1659 Treaty of Pyrenees. Because of its highly strategic importance, the town's fortifications, the Château Royal de Collioure and the Fort Saint-Elme stronghold, were improved by the military engineer Vauban during the reign of Louis XIV. Nevertheless, Collioure was besieged and occupied by the Spanish troops in 1793, marking the last Spanish attempt to take the city. The city was retaken a year later by general Jacques François Dugommier.
In 1823, the territory of Port-Vendres became a commune, taking parts from the communes of Collioure and Banyuls-sur-Mer.[5]
On 21 January 1870, an exceptional climatic phenomenon occurred in Collioure, as observed by Charles Naudin at the time; more than one metre (39 inches) of snow fell in one day on the town. Many orchards as well as cork oak woodlands were damaged.[6]
Government and politics
Mayors
| Mayor | Term start | Term end |
|---|---|---|
| Michel Noë | 1864 | 1870 |
| Jean Cortade | 1870 | 1874 |
| Jean Caloni | 1874 | 1878 |
| Jean Coste[7] | 1878 | 1903 |
| Joseph Rossines | 1903 | 1919 |
| Marceau Banyuls | 1948 | 1953 |
| Vincent Atxer | 1953 | 1956 |
| Henri Billard | 1956 | 1956 |
| René Ramona | 1956 | 1966 |
| Joseph Py | 1966 | 1977 |
| Jean Pascot | 1977 | 1989 |
| Michel Moly | 1989 | 2014 |
| Jacques Manya | 2014 |
Twin city
Population
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1968 | 2,525 | — |
| 1975 | 2,516 | −0.05% |
| 1982 | 2,527 | +0.06% |
| 1990 | 2,726 | +0.95% |
| 1999 | 2,763 | +0.15% |
| 2007 | 2,944 | +0.80% |
| 2012 | 3,082 | +0.92% |
| 2017 | 2,427 | −4.67% |
| Source: INSEE[8] | ||
Economy
Collioure is the name of an Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée (AOC) situated around the town, (Collioure AOC), producing red, rosé and a few white wines. The ancient terraced vines in the hills behind the town also provide grapes for the apéritif and dessert wines of the (Banyuls) appellation, which shares its boundaries with the Collioure appellation.
Collioure is also famous for its anchovies, and its once-thriving fisheries are referenced in Mark Kurlansky's book Salt.
Culture
As the town has a strong Catalan culture, its own motto has been adopted by one of the local Catalan rugby teams (USA Perpignan, France): Sempre endavant, mai morirem (Always forward, We'll never die). Under Michel Moly's leadership, the town has an alternative motto, Collioure sera toujours Collioure (Collioure shall always be Collioure) quoting French singer Maurice Chevalier's famous song titled Paris sera toujours Paris.
The annual Saint Vincent festival is held around August 15, attracting twice the town's population in visitors for several days of celebration with music and fireworks.[9]
In the early 20th century Collioure became a center of artistic activity, with several Fauve artists making it their meeting place. André Derain, Georges Braque, Othon Friesz, Henri Matisse, Pablo Picasso, Charles Rennie Mackintosh, James Dickson Innes and Tsuguharu Fujita have all been inspired by Collioure's royal castle, medieval streets, its lighthouse converted into the church of Notre-Dame-des-Anges and its typical Mediterranean bay. Collioure's cemetery contains the tomb of Spanish poet Antonio Machado, who fled here to escape advancing Francoist troops at the end of the Spanish Civil War in 1939.
The British novelist Patrick O'Brian lived in the town from 1949 until his death in 2000, and his novel The Catalans describes Collioure life as it was in the past. He also wrote a biography of Picasso, who was an acquaintance. O'Brian and his wife Mary are also buried in the town cemetery.
The start of Rose Macaulay’s 1950 novel, The World My Wilderness, is set in Collioure.
Part of the action in Stephen Clarke's fourth comic novel featuring Paul West, Dial M for Merde, takes place in Collioure.
Ninety-eight reproductions of Matisse’s and Derain’s works are displayed exactly where these two masters of Fauvism painted the originals in the early 20th century.
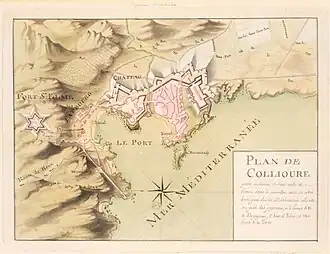 Map of Collioure (18th century)
Map of Collioure (18th century) Collioure's church, Notre-Dame-des-Anges
Collioure's church, Notre-Dame-des-Anges Château Royal de Collioure
Château Royal de Collioure Fort Carré
Fort Carré Tour de l' Étoile
Tour de l' Étoile Collioure, seen from the south-east
Collioure, seen from the south-east
Notable people

- Nur Ali Sheikh (1928-), Kenyan-born neo-cubist painter who lived in the house depicted by Matisse in his View of Collioure
- René Llense (1913-2014), football player born in Collioure.
- Antonio Machado (1875-1939), Spanish poet died in Collioure.
- Patrick O'Brian (1914-2000), English novelist and translator, lived and was buried in Collioure.
See also
References
- ↑ "Répertoire national des élus: les maires". data.gouv.fr, Plateforme ouverte des données publiques françaises (in French). 2 December 2020.
- ↑ "Populations légales 2021". The National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies. 28 December 2023.
- ↑ INSEE commune file
- ↑ (in Catalan and French) Nomenclàtor toponímic de la Catalunya del Nord, Institut d’Estudis Catalans, Université de Perpignan, 2007
- ↑ Jean-Pierre Pélissier, Paroisses et communes de France : dictionnaire d'histoire administrative et démographique, vol. 66 : Pyrénées-Orientales, Paris, CNRS, 1986
- ↑ Cárdenas, Fabricio (2014). 66 petites histoires du Pays Catalan [66 Little Stories of Catalan Country] (in French). Perpignan: Ultima Necat. ISBN 978-2-36771-006-8. OCLC 893847466.
- ↑ Cardenas, Fabricio (31 October 2014). "Démission du maire de Collioure en 1885". Vieux papiers des Pyrénées-Orientales (in French). Retrieved 24 April 2016.
- ↑ Population en historique depuis 1968, INSEE
- ↑ "Festival programme 2012" (in French). Archived from the original on 8 November 2012. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
External links
- Tourist office website
- Webpage about the fortifications of Collioure
- Photos of Collioure
- (in French) Information of the Royal Castle of Collioure
- Cotlliure History and information in Catalan Encyclopaedia.