 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | MMC; Superlutin caproate; Methenmadinone hexanoate; Lutofollin; 17α-Hydroxy-16-methyl-6-dehydroprogesterone caproate; 17α-Hydroxy-16-methylpregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione 17α-hexanoate |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Progestogen; Progestin; Progestogen ester |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C28H38O4 |
| Molar mass | 438.608 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
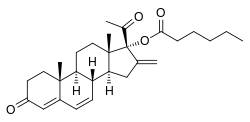
Methenmadinone caproate (MMC, also known as superlutin caproate) is a progestin medication which was developed in Czechoslovakia in the 1960s and was studied for potential use in combined injectable contraceptives in the 1970s but was never marketed.[1][2][3][4] It was studied as a combined injectable contraceptive in combination with estradiol valerate at doses of 60 mg and 10 mg, respectively, once a month by intramuscular injection (tentative brand name Lutofollin).[2][3][4] MMC is the C17α caproate (hexanoate) ester of methenmadinone and an analogue of methenmadinone acetate (MMA; superlutin).[5][6][1][7] In addition to MMA, analogues of MMC include chlormadinone caproate, gestonorone caproate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone caproate, and megestrol caproate.
See also
References
- 1 2 Syhora K, Mazáč R (1964). "Steroid derivatives. XXXI. A novel synthesis of 16-methylene-17α-acyloxy-20-ketopregnane derivatives". Collection of Czechoslovak Chemical Communications. 29 (10): 2351–2359. doi:10.1135/cccc19642351. ISSN 0010-0765.
- 1 2 Stĕrba R (1976). "[A Czechoslovak injection-contraceptive agent administered once a month]". Zentralblatt Fur Gynakologie (in German). 98 (3): 158–160. PMID 970015.
- 1 2 Toppozada MK (April 1994). "Existing once-a-month combined injectable contraceptives". Contraception. 49 (4): 293–301. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(94)90029-9. PMID 8013216.
- 1 2 Toppozada MK (1983). "Monthly Injectable Contraceptives". In Goldsmith A, Toppozada M (eds.). Long-Acting Contraception. pp. 93–103. OCLC 35018604.
- ↑ Milne GW (1 November 2017). Ashgate Handbook of Endocrine Agents and Steroids. Taylor & Francis. pp. 158–. ISBN 978-1-351-74347-1.
- ↑ Milne GW (8 May 2018). Drugs: Synonyms and Properties: Synonyms and Properties. Taylor & Francis. pp. 1572–. ISBN 978-1-351-78989-9.
- ↑ Shapiro EL, Weber L, Harris H, Miskowicz C, Neri R, Herzog HL (July 1972). "Synthesis and biological activity of 17-esters of 6-dehydro-16-methylene-17 -hydroxyprogesterones". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 15 (7): 716–720. doi:10.1021/jm00277a006. PMID 5043870.