| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Trifluoro-λ3-chlorane[1] (substitutive) | |||
| Other names
Chlorotrifluoride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.301 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 1439 | |||
| MeSH | chlorine+trifluoride | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1749 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| ClF3 | |||
| Molar mass | 92.45 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas or greenish-yellow liquid | ||
| Odor | Sweet, pungent, irritating, suffocating[2][3] | ||
| Density | 3.779 g/L[4] | ||
| Melting point | −76.34 °C (−105.41 °F; 196.81 K)[4] | ||
| Boiling point | 11.75 °C (53.15 °F; 284.90 K)[4] (decomposes at 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K)) | ||
| Reacts with water[1] | |||
| Solubility | Soluble in carbon tetrachloride but explosive in high concentrations. Reacts with hydrogen-containing compounds e.g. hydrogen, methane, benzene, ether, ammonia.[1] | ||
| Vapor pressure | 175 kPa | ||
| −26.5×10−6 cm3/mol[5] | |||
| Viscosity | 91.82 μPa s | ||
| Structure | |||
| T-shaped molecular geometry | |||
| Thermochemistry[6] | |||
Heat capacity (C) |
63.9 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std molar entropy (S⦵298) |
281.6 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−163.2 kJ mol−1 | ||
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵) |
−123.0 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards |
Very toxic, very corrosive, powerful oxidizer, violent hydrolysis[3] | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
    | |||
| Danger | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | noncombustible[3] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (median concentration) |
95 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 178 ppm (mouse, 1 hr) 230 ppm (monkey, 1 hr) 299 ppm (rat, 1 hr) [7] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible) |
C 0.1 ppm (0.4 mg/m3)[3] | ||
REL (Recommended) |
C 0.1 ppm (0.4 mg/m3)[3] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
20 ppm[3] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
Chlorine pentafluoride Chlorine monofluoride | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Chlorine trifluoride is an interhalogen compound with the formula ClF3. This colorless, poisonous, corrosive, and extremely reactive gas condenses to a pale-greenish yellow liquid, the form in which it is most often sold (pressurized at room temperature). Despite being famous for its extreme oxidation properties and igniting many things, chlorine trifluoride is not combustible itself. The compound is primarily of interest in plasmaless cleaning and etching operations in the semiconductor industry,[8][9] in nuclear reactor fuel processing,[10] historically as a component in rocket fuels, and various other industrial operations owing to its corrosive nature.[11]
Preparation, structure, and properties
It was first reported in 1930 by Ruff and Krug who prepared it by fluorination of chlorine; this also produced Chlorine monofluoride (ClF) and the mixture was separated by distillation.[12]
- 3 F2 + Cl2 → 2 ClF3
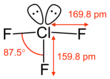
The molecular geometry of ClF3 is approximately T-shaped, with one short bond (1.598 Å) and two long bonds (1.698 Å).[13] This structure agrees with the prediction of VSEPR theory, which predicts lone pairs of electrons as occupying two equatorial positions of a hypothetic trigonal bipyramid. The elongated Cl-F axial bonds are consistent with hypervalent bonding.
Pure ClF3 is stable to 180 °C (356 °F) in quartz vessels; above this temperature, it decomposes by a free radical mechanism to its constituent elements.
Reactions
Reactions with many metals give chlorides and fluorides. With phosphorus, it yields phosphorus trichloride (PCl3) and phosphorus pentafluoride (PF5), while sulfur yields sulfur dichloride (SCl2) and sulfur tetrafluoride (SF4). ClF3 also reacts with water to give hydrogen fluoride and hydrogen chloride, along with oxygen and oxygen difluoride (OF2):
- ClF3 + H2O → HF + HCl + OF2
- ClF3 + 2H2O → 3HF + HCl + O2
It will also convert many metal oxides to metal halides and oxygen or oxygen difluoride.
It occurs as a ligand in the complex CsF(ClF3)3.[14]
One of the main uses of ClF3 is to produce uranium hexafluoride, UF6, as part of nuclear fuel processing and reprocessing, by the fluorination of uranium metal:
- U + 3 ClF3 → UF6 + 3 ClF
The compound can also dissociate under the scheme:
- ClF3 → ClF + F2
Uses
Semiconductor industry
In the semiconductor industry, chlorine trifluoride is used to clean chemical vapour deposition chambers.[15] It has the advantage that it can be used to remove semiconductor material from the chamber walls without the need to dismantle the chamber.[15] Unlike most of the alternative chemicals used in this role, it does not need to be activated by the use of plasma since the heat of the chamber is sufficient to make it decompose and react with the semiconductor material.[15]
Rocket propellant
Chlorine trifluoride has been investigated as a high-performance storable oxidizer in rocket propellant systems. Handling concerns, however, severely limit its use. The following passage by rocket scientist John D. Clark is widely quoted in descriptions of the substance's extremely hazardous nature:
It is, of course, extremely toxic, but that's the least of the problem. It is hypergolic with every known fuel, and so rapidly hypergolic that no ignition delay has ever been measured. It is also hypergolic with such things as cloth, wood, and test engineers, not to mention asbestos, sand, and water—with which it reacts explosively. It can be kept in some of the ordinary structural metals—steel, copper, aluminum, etc.—because of the formation of a thin film of insoluble metal fluoride that protects the bulk of the metal, just as the invisible coat of oxide on aluminium keeps it from burning up in the atmosphere. If, however, this coat is melted or scrubbed off, and has no chance to reform, the operator is confronted with the problem of coping with a metal-fluorine fire. For dealing with this situation, I have always recommended a good pair of running shoes.[16]
Chlorine pentafluoride (ClF5) has also been investigated as a potential rocket oxidizer. It offered improved specific impulse over chlorine trifluoride, but with all of the same difficulties in handling. Neither compound has been used in any operational rocket propulsion system.
Proposed military applications
Under the code name N-Stoff ("substance N"), chlorine trifluoride was investigated for military applications by the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute in Nazi Germany not long before the start of World War II. Tests were made against mock-ups of the Maginot Line fortifications, and it was found to be an extremely effective incendiary weapon and poison gas. From 1938, construction commenced on a partly bunkered, partly subterranean 14,000 m2 (150,000 sq ft) munitions factory, the Falkenhagen industrial complex, which was intended to produce 90 tonnes of N-Stoff per month, in addition to sarin (a deadly nerve agent). However, by the time it was captured by the advancing Red Army in 1945, the factory had produced only about 30 to 50 tonnes, at a cost of over 100 German Reichsmarks per kilogram.a N-Stoff was never used in war.[17][18]
Hazards
ClF3 is a very strong oxidizer, specifically a fluorinating agent. It is extremely reactive with most inorganic and organic materials, and will combust many otherwise non-flammable materials without any ignition source. These reactions are often violent, and in some cases explosive, especially with flammable materials. Steel, copper, and nickel are not consumed because a passivation layer of insoluble metal fluoride will form which prevents further corrosion, but molybdenum, tungsten, and titanium are unsuitable as the fluorides that they form are volatile. Any equipment that comes into contact with ClF3 must be meticulously cleaned and then passivated, because any contamination left may burn through the unfluorinated material faster than it can re-form. ClF3 will quickly corrode even noble metals like iridium, platinum, or gold, oxidizing them to chlorides and fluorides.
This oxidizing power, surpassing that of oxygen, causes ClF3 to react vigorously with many other materials often thought of as incombustible and refractory. It is known to ignite sand, asbestos, glass, and even ashes of substances that have already burned in oxygen. In one particular industrial accident, a spill of 900 kg of ClF3 burned through 30 cm of concrete and 90 cm of gravel beneath.[19][16] There is exactly one known fire control/suppression method capable of dealing with ClF3—flooding the fire with nitrogen or noble gases such as argon. Barring that, the area must simply be kept cool until the reaction ceases.[20] The compound reacts with water-based suppressors and CO2, rendering them counterproductive.[21]
Exposure to larger amounts of ClF3, as a liquid or as a gas, ignites living tissue, resulting in severe chemical and thermal burns. ClF3 reacts violently with water and exposure to the reaction also results in burns. The products of hydrolysis are mainly hydrofluoric acid and hydrochloric acid, which are usually released as steam or vapor due to the highly exothermic nature of the reaction.
See also
Explanatory notes
^a Using data from Economic History Services[22] and The Inflation Calculator[23] it can be calculated that the sum of 100 Reichsmarks in 1941 is approximately equivalent to US$4,652.50 in 2021. Reichsmark exchange rate values from 1942 to 1944 are fragmentary.
References
- 1 2 3 "Chlorine trifluoride". PubChem Compound. National Center for Biotechnology Information. 4 July 2023. Retrieved 8 July 2023.
- ↑ ClF3/Hydrazine Archived 2007-02-02 at the Wayback Machine at the Encyclopedia Astronautica.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0117". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 3 Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). CRC Press. p. 4.58. ISBN 978-1-4398-5511-9.
- ↑ Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). CRC Press. p. 4.132. ISBN 978-1-4398-5511-9.
- ↑ Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). CRC Press. p. 5.8. ISBN 978-1-4398-5511-9.
- ↑ "Chlorine trifluoride". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Habuka, Hitoshi; Sukenobu, Takahiro; Koda, Hideyuki; Takeuchi, Takashi; Aihara, Masahiko (2004). "Silicon Etch Rate Using Chlorine Trifluoride". Journal of the Electrochemical Society. 151 (11): G783–G787. Bibcode:2004JElS..151G.783H. doi:10.1149/1.1806391. Archived from the original on 2022-01-25. Retrieved 2017-04-11.
- ↑ Xi, Ming et al. (1997) U.S. Patent 5,849,092 "Process for chlorine trifluoride chamber cleaning"
- ↑ Board on Environmental Studies and Toxicology, (BEST) (2006). Acute Exposure Guideline Levels for Selected Airborne Chemicals: Volume 5. Washington D.C.: National Academies Press. p. 40. ISBN 978-0-309-10358-9. (available from National Academies Press Archived 2014-11-07 at the Wayback Machine
 )
) - ↑ Boyce, C. Bradford and Belter, Randolph K. (1998) U.S. Patent 6,034,016 "Method for regenerating halogenated Lewis acid catalysts"
- ↑ Otto Ruff, H. Krug (1930). "Über ein neues Chlorfluorid-CIF3". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 190 (1): 270–276. doi:10.1002/zaac.19301900127.
- ↑ Smith, D. F. (1953). "The Microwave Spectrum and Structure of Chlorine Trifluoride". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 21 (4): 609–614. Bibcode:1953JChPh..21..609S. doi:10.1063/1.1698976. hdl:2027/mdp.39015095092865.
- ↑ Scheibe, Benjamin; Karttunen, Antti J.; Müller, Ulrich; Kraus, Florian (5 October 2020). "Cs[Cl 3 F 10 ]: A Propeller‐Shaped [Cl 3 F 10 ] − Anion in a Peculiar A [5] B [5] Structure Type". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 59 (41): 18116–18119. doi:10.1002/anie.202007019. PMC 7589245. PMID 32608053.
- 1 2 3 "In Situ Cleaning of CVD Chambers". Semiconductor International. June 1, 1999.
- 1 2 Clark, John D. (1972). Ignition! An Informal History of Liquid Rocket Propellants. Rutgers University Press. p. 214. ISBN 978-0-8135-0725-5.
- ↑ Müller, Benno (24 November 2005). "A poisonous present". Nature. Review of: Kampfstoff-Forschung im Nationalsozialismus: Zur Kooperation von Kaiser-Wilhelm-Instituten, Militär und Industrie [Weapons Research in National Socialism] by Florian Schmaltz (Wallstein, 2005, 676 pages). 438 (7067): 427. Bibcode:2005Natur.438..427M. doi:10.1038/438427a.
- ↑ "Germany 2004". www.bunkertours.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2006-06-13. Retrieved 2006-06-13.
- ↑ Safetygram. Air Products
- ↑ "Chlorine Trifluoride Handling Manual". Canoga Park, CA: Rocketdyne. September 1961. p. 24. Archived from the original on 2013-04-08. Retrieved 2012-09-19.
- ↑ Patnaik, Pradyot (2007). A comprehensive guide to the hazardous properties of chemical substances (3rd ed.). Wiley-Interscience. p. 478. ISBN 978-0-471-71458-3.
- ↑ Officer, Lawrence H. (2002), Exchange Rate Between the United States Dollar and Forty Other Countries, 1913–1999, EH.net (Economic History Services), archived from the original on 15 June 2006, retrieved 7 July 2023
- ↑ "The Inflation Calculator". S. Morgan Friedman's 'Webpage': Ceci N'est Pas Une Homepage. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
Further reading
- Groehler, Olaf (1989). Der lautlose Tod. Einsatz und Entwicklung deutscher Giftgase von 1914 bis 1945. Reinbek bei Hamburg: Rowohlt. ISBN 978-3-499-18738-4.
- Ebbinghaus, Angelika (1999). Krieg und Wirtschaft: Studien zur deutschen Wirtschaftsgeschichte 1939–1945. Berlin: Metropol. pp. 171–194. ISBN 978-3-932482-11-3.
- Booth, Harold Simmons; Pinkston, John Turner Jr. (1947). "The Halogen Fluorides". Chemical Reviews. 41 (3): 421–439. doi:10.1021/cr60130a001. PMID 18895518.
- Yu D Shishkov; A A Opalovskii (1960). "Physicochemical Properties of Chlorine Trifluoride". Russian Chemical Reviews. 29 (6): 357–364. Bibcode:1960RuCRv..29..357S. doi:10.1070/RC1960v029n06ABEH001237. S2CID 250863587.
- Robinson D. Burbank; Frank N. Bensey (1953). "The Structures of the Interhalogen Compounds. I. Chlorine Trifluoride at −120 °C". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 21 (4): 602–608. Bibcode:1953JChPh..21..602B. doi:10.1063/1.1698975.
- A. A. Banks; A. J. Rudge (1950). "The determination of the liquid density of chlorine trifluoride". Journal of the Chemical Society: 191–193. doi:10.1039/JR9500000191.
- Lowdermilk, F. R.; Danehower, R. G.; Miller, H. C. (1951). "Pilot plant study of fluorine and its derivatives". Journal of Chemical Education. 28 (5): 246. Bibcode:1951JChEd..28..246L. doi:10.1021/ed028p246.