| Solar eclipse of April 29, 1976 | |
|---|---|
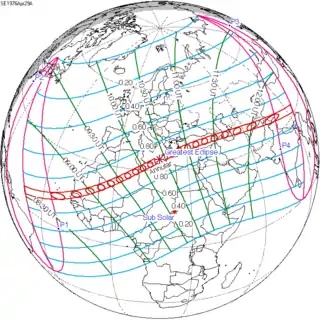 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | 0.3378 |
| Magnitude | 0.9421 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 401 sec (6 m 41 s) |
| Coordinates | 34°00′N 18°18′E / 34°N 18.3°E |
| Max. width of band | 227 km (141 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 10:24:18 |
| References | |
| Saros | 128 (56 of 73) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9456 |
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on Thursday, April 29, 1976. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from North Africa, Greece, Turkey, Middle East, central Asia, India, China. 5 of the 14 eight-thousanders in Pakistan and China—Nanga Parbat, K2, Broad Peak, Gasherbrum II and Gasherbrum I, lie in the path of annularity.
Observation
The Institute of Physics and Institute of Mathematics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Xinjiang Earthquake Team conducted observations of gravitational effects using gravimeters, inclinometers, pendulum clocks and seismometers in southwestern Hotan County, Hotan Prefecture, Xinjiang near the Karakoram Pass at an altitude of 5,500 metres (18,000 ft). Results showed that the gravitational acceleration had no obvious effect within the accuracy of the instruments. No inclination was recorded on the photosensitive paper of the inclinometer due to the width of its lines. Three inclinations were pen-recorded, whose time and direction were clearly related to that of the eclipse. Due to the difficult conditions with the high altitude, the observation team was unable to obtain more comparative data.[1]
Related eclipses
Eclipses in 1976
- An annular solar eclipse on Thursday, 29 April 1976.
- A partial lunar eclipse on Thursday, 13 May 1976.
- A total solar eclipse on Saturday, 23 October 1976.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on Saturday, 6 November 1976.
Solar eclipses of 1975–1978
There were 8 solar eclipses (at 6 month intervals) between May 11, 1975 and October 2, 1978.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1975–1978 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 118 | 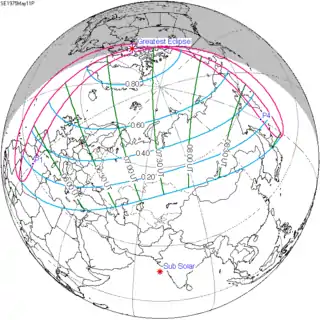 1975 May 11 Partial | 1.06472 | 123 | 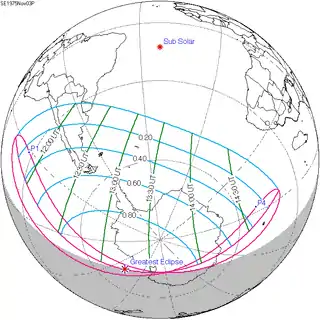 1975 November 3 Partial | −1.02475 | |
| 128 |  1976 April 29 Annular | 0.33783 | 133 | 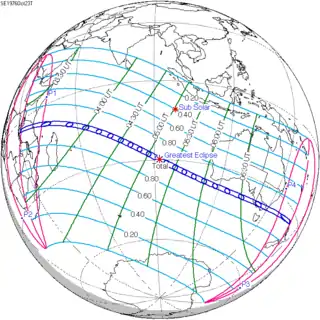 1976 October 23 Total | −0.32699 | |
| 138 | 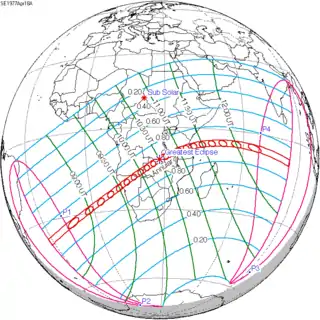 1977 April 18 Annular | −0.39903 | 143 | 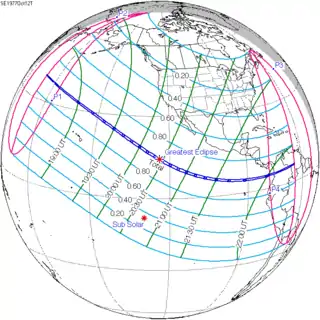 1977 October 12 Total | 0.38363 | |
| 148 | 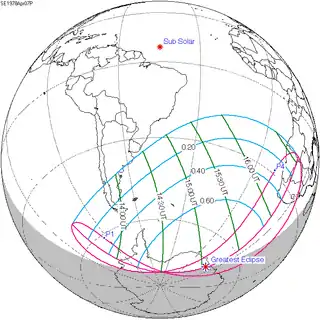 1978 April 7 Partial | −1.10812 | 153 |  1978 October 2 Partial | 1.16164 | |
Saros 128
This eclipse is a member of the Solar Saros cycle 128, which includes 73 eclipses occurring in intervals of 18 years and 11 days. The series started with partial solar eclipse on August 29, 984 AD. From May 16, 1417 through June 18, 1471 the series produced total solar eclipses, followed by hybrid solar eclipses from June 28, 1489 through July 31, 1543, and annular solar eclipses from August 11, 1561 through July 25, 2120. The series ends at member 73 as a partial eclipse on November 1, 2282. All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon’s descending node.
| Series members 52–68 occur between 1901 and 2200 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 52 | 53 | 54 |
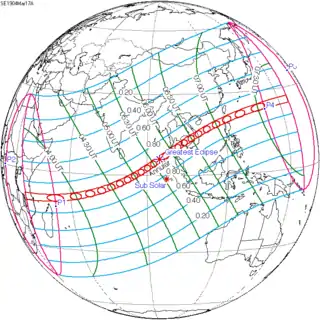 March 17, 1904 |
 March 28, 1922 |
 April 7, 1940 |
| 55 | 56 | 57 |
 April 19, 1958 |
 April 29, 1976 |
 May 10, 1994 |
| 58 | 59 | 60 |
 May 20, 2012 |
 June 1, 2030 |
 June 11, 2048 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 |
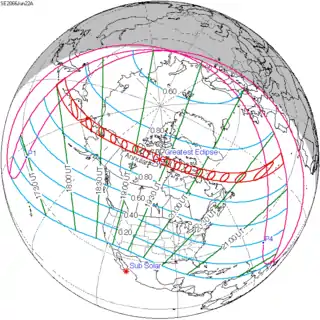 June 22, 2066 |
 July 3, 2084 |
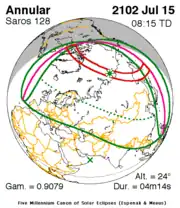 July 15, 2102 |
| 64 | 65 | 66 |
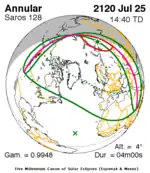 July 25, 2120 |
August 5, 2138 (Partial) | August 16, 2156 (Partial) |
| 67 | 68 | |
| August 27, 2174 (Partial) | September 6, 2192 (Partial) | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 21 eclipse events, progressing from north to south between July 11, 1953 and July 11, 2029 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 10–12 | April 29–30 | February 15–16 | December 4–5 | September 21–23 |
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
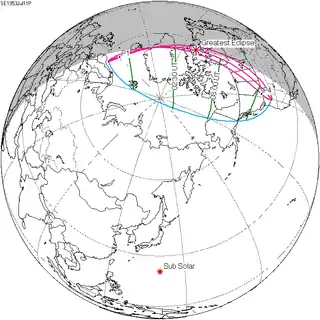 July 11, 1953 |
 April 30, 1957 |
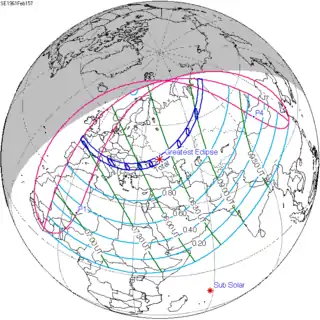 February 15, 1961 |
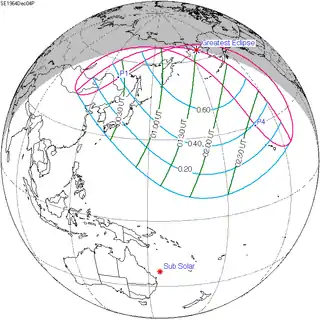 December 4, 1964 |
 September 22, 1968 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
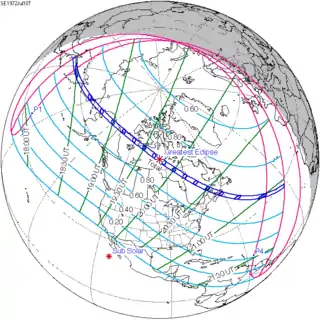 July 10, 1972 |
 April 29, 1976 |
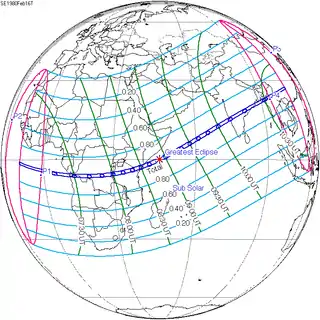 February 16, 1980 |
 December 4, 1983 |
 September 23, 1987 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
 July 11, 1991 |
 April 29, 1995 |
 February 16, 1999 |
 December 4, 2002 |
 September 22, 2006 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
 July 11, 2010 |
 April 29, 2014 |
 February 15, 2018 |
 December 4, 2021 |
 September 21, 2025 |
| 156 | 158 | 160 | 162 | 164 |
 July 11, 2029 | ||||
Notes
- ↑ 王榴泉 田景发 刘煜奋 汤小琳 赵之淑 秦荣先 谭大均 刘易成 张建朝 (1978). "1976年4月29日日环食时引力效应观测——重力仪与倾斜仪的观测结果". 科学通报 (8): 477–480.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Solar eclipse of April 29, 1976 in Russia Archived August 9, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
.jpg.webp)

