| Solar eclipse of October 1, 1921 | |
|---|---|
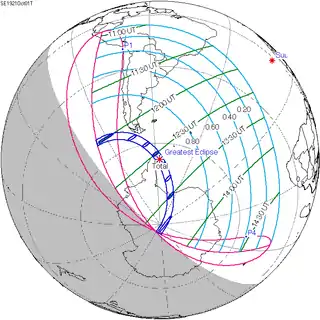 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | −0.9383 |
| Magnitude | 1.0293 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 112 sec (1 m 52 s) |
| Coordinates | 66°06′S 56°06′W / 66.1°S 56.1°W |
| Max. width of band | 291 km (181 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 12:35:58 |
| References | |
| Saros | 123 (48 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9331 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on October 1, 1921. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1921–1924
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1921–1924 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||
| 118 | April 8, 1921 Annular |
123 | October 1, 1921 Total | |
| 128 | March 28, 1922 Annular |
133 | September 21, 1922 Total | |
| 138 | March 17, 1923 Annular |
143 | September 10, 1923 Total | |
| 148 | March 5, 1924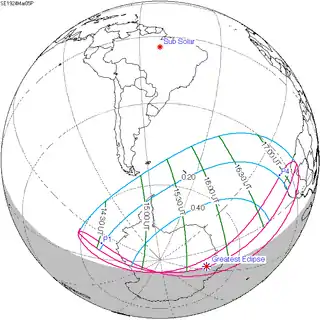 Partial |
153 | August 30, 1924 Partial | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 22 eclipse events between December 13, 1898 and July 20, 1982 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| December 13–14 | October 1–2 | July 20–21 | May 9 | February 24–25 |
| 111 | 113 | 115 | 117 | 119 |
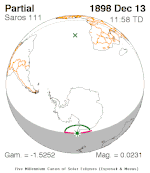 December 13, 1898 |
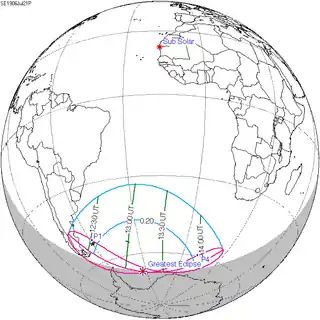 July 21, 1906 |
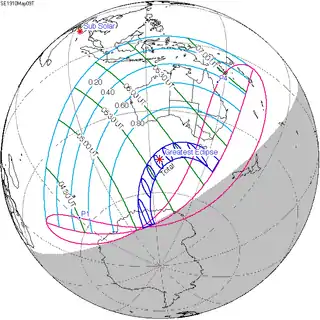 May 9, 1910 |
 February 25, 1914 | |
| 121 | 123 | 125 | 127 | 129 |
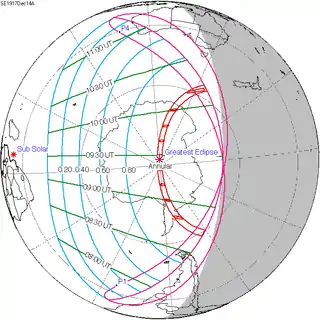 December 14, 1917 |
 October 1, 1921 |
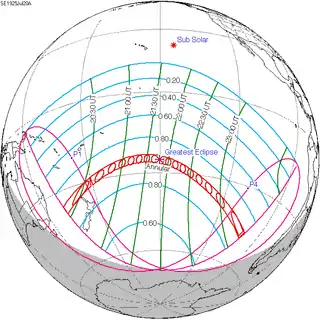 July 20, 1925 |
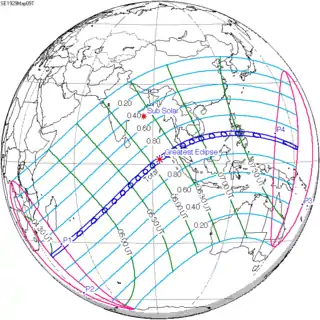 May 9, 1929 |
 February 24, 1933 |
| 131 | 133 | 135 | 137 | 139 |
 December 13, 1936 |
 October 1, 1940 |
 July 20, 1944 |
 May 9, 1948 |
 February 25, 1952 |
| 141 | 143 | 145 | 147 | 149 |
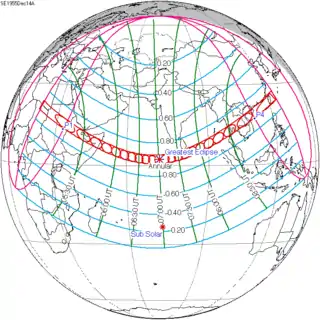 December 14, 1955 |
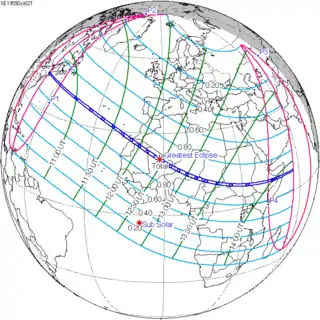 October 2, 1959 |
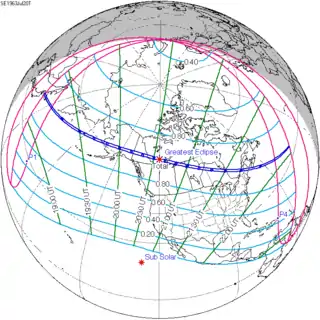 July 20, 1963 |
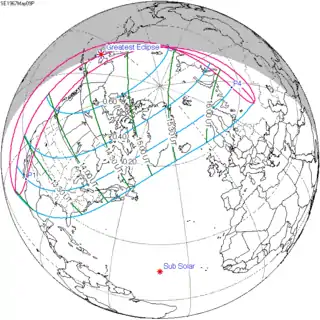 May 9, 1967 |
 February 25, 1971 |
| 151 | 153 | 155 | ||
 December 13, 1974 |
 October 2, 1978 |
 July 20, 1982 | ||
Notes
- ↑ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
.jpg.webp)

