| Solar eclipse of October 14, 2004 | |
|---|---|
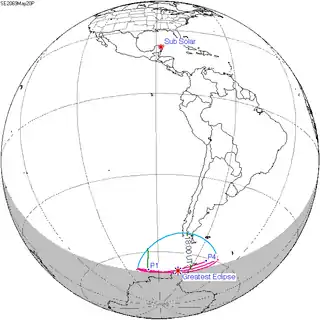
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | 1.0348 |
| Magnitude | 0.9282 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 61°12′N 153°42′W / 61.2°N 153.7°W |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 3:00:23 |
| References | |
| Saros | 124 (54 of 73) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9518 |
A partial solar eclipse occurred on October 13–14, 2004.[1][2] A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. It was the 54th eclipse of the 124th Saros cycle, which began with a partial eclipse on March 6, 1049 and will conclude with a partial eclipse on May 11, 2347.
Images
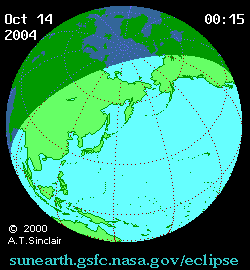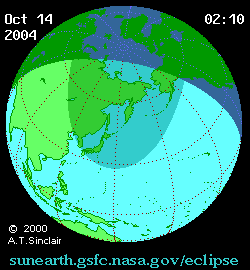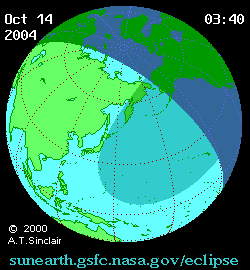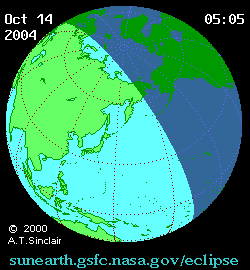
Animated path
Related eclipses
Eclipse season
This is the first eclipse this season.
Second eclipse this season: 28 October 2004 Total Lunar Eclipse
Eclipses of 2004
- A partial solar eclipse on April 19.
- A total lunar eclipse on May 4.
- A partial solar eclipse on October 14.
- A total lunar eclipse on October 28.
Saros 124
Solar saros 124, repeating every about 18 years and 11 days, contains 73 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on March 6, 1049. It contains total eclipses from June 12, 1211, to September 22, 1968, and a hybrid solar eclipse on October 3, 1986. The series ends at member 73 as a partial eclipse on May 11, 2347. The longest total eclipse occurred on May 3, 1734, at 5 minutes and 46 seconds.[3]
| Series members 43–59 occur between 1801 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 43 | 44 | 45 |
 June 16, 1806 |
 June 26, 1824 |
 July 8, 1842 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 |
 July 18, 1860 |
 July 29, 1878 |
 August 9, 1896 |
| 49 | 50 | 51 |
 August 21, 1914 |
 August 31, 1932 |
 September 12, 1950 |
| 52 | 53 | 54 |
 September 22, 1968 |
 October 3, 1986 |
 October 14, 2004 |
| 55 | 56 | 57 |
 October 25, 2022 |
 November 4, 2040 |
 November 16, 2058 |
| 58 | 59 | |
 November 26, 2076 |
 December 7, 2094 | |
Solar eclipses 2004–2007
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[4]
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 119 | 2004 April 19 Partial (south) |
−1.13345 | 124 | 2004 October 14 Partial (north) |
1.03481 | |
129_(cropped).jpg.webp) Partial from Naiguatá |
2005 April 08 Hybrid |
−0.34733 | 134 Annular from Madrid, Spain |
2005 October 03 Annular |
0.33058 | |
139 Total from Side, Turkey |
2006 March 29 Total |
0.38433 | 144.jpg.webp) Partial from São Paulo, Brazil |
2006 September 22 Annular |
−0.40624 | |
149_(cropped).jpg.webp) From Jaipur, India |
2007 March 19 Partial (north) |
1.07277 | 154_(cropped).jpg.webp) From Córdoba, Argentina |
2007 September 11 Partial (south) |
−1.12552 | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.[5]
| Octon series with 21 events between May 21, 1993 and August 2, 2065 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 20–21 | March 8–9 | December 25–26 | October 13–14 | August 1–2 |
| 98 | 100 | 102 | 104 | 106 |
| May 21, 1955 | March 9, 1959 | December 26, 1962 | October 14, 1966 | August 2, 1970 |
| 108 | 110 | 112 | 114 | 116 |
| May 21, 1974 | March 9, 1978 | December 26, 1981 | October 14, 1985 | August 1, 1989 |
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
 May 21, 1993 |
 March 9, 1997 |
 December 25, 2000 |
 October 14, 2004 |
 August 1, 2008 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
 May 20, 2012 |
 March 9, 2016 |
 December 26, 2019 |
 October 14, 2023 |
 August 2, 2027 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
 May 21, 2031 |
 March 9, 2035 |
 December 26, 2038 |
 October 14, 2042 |
 August 2, 2046 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | 156 |
 May 20, 2050 |
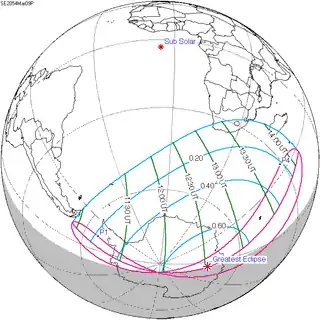 March 9, 2054 |
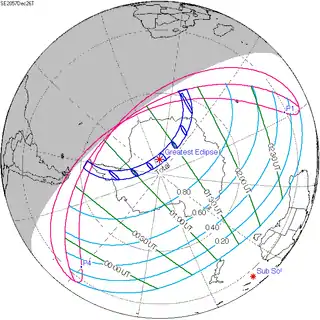 December 26, 2057 |
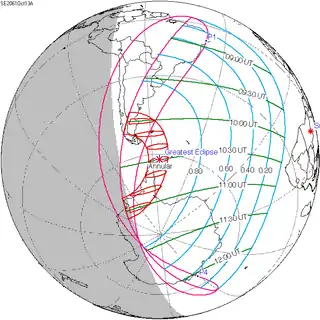 October 13, 2061 |
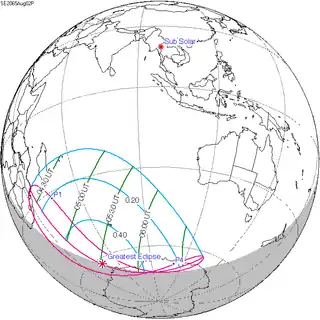 August 2, 2065 |
| 158 | 160 | 162 | 164 | 166 |
 May 20, 2069 |
March 8, 2073 | December 26, 2076 | October 13, 2080 | August 1, 2084 |
References
- ↑ "'Almost eclipse' will be in this afternoon's sky". Pacific Daily News. 2004-10-14. p. 37. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ↑ "Sky Watch". Albuquerque Journal. 2004-10-13. p. 22. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ↑ Saros Series Catalog of Solar Eclipses NASA Eclipse Web Site.
- ↑ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ↑ Note S1: Eclipses & Predictions in Freeth, Tony (2014). "Eclipse Prediction on the Ancient Greek Astronomical Calculating Machine Known as the Antikythera Mechanism". PLOS ONE. 9 (7): e103275. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j3275F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0103275. PMC 4116162. PMID 25075747.
External links
Photos:
- Spaceweather.com eclipse gallery
- Partial Solar Eclipse on October 14, 2004, Nagoya, Aichi, Japan by Toshimi Taki
- Report (0,371 max.phase) from Khabarovsk, Russia
.jpg.webp)

