| Solar eclipse of August 9, 1896 | |
|---|---|
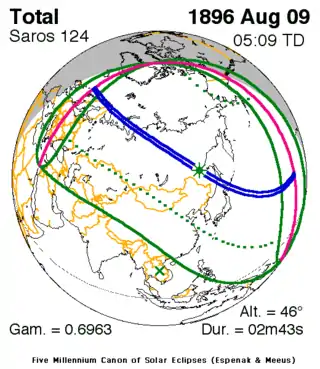 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.6964 |
| Magnitude | 1.0392 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 163 sec (2 m 43 s) |
| Coordinates | 54°24′N 132°12′E / 54.4°N 132.2°E |
| Max. width of band | 182 km (113 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 5:09:00 |
| References | |
| Saros | 124 (48 of 73) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9272 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on August 9, 1896. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. It was visible across Europe, Asia, and Japan.
It is a part of solar Saros 124.
This event was the subject of the first organized eclipse expedition by the British Astronomical Association. A group of 165 amateur and profession astronomers sailed from Tilbury, England on July 25, heading toward Vadsø, Norway.[1] This expedition failed to produce any usable results as they were frustrated by the weather conditions at the time of the eclipse.[2] However, a smaller expedition to Novaya Zemlya on Sir George Baden-Powell's yacht Otario met with success.[1]
Gallery
References
- 1 2 Marriott, R. A. (June 1991). "Norway 1896: the BAA's first organised eclipse expedition". Journal of the British Astronomical Association. 101 (3): 162–170. Bibcode:1991JBAA..101..162M.
- ↑ "Expedition for the Observation of the Total Solar Eclipse, August 9th, 1896". Memoirs of the British Astronomical Association. 6: 1–4. 1898. Bibcode:1898MmBAA...6....1.
External links
- NASA graphics
- Corona and Coronet: Being a narrative of the Amherst Eclipse Expedition to Japan, in Mr. James's Schooner-Yacht Coronet, to Observe the Sun's Total Obscuration, 9th August, 1896, by Mabel Loomis Todd, Houghton, Mifflin and Company, publishers, 1898
- Mabel Loomis Todd (1900). Total Eclipses of the Sun. Little, Brown.
- Solar eclipse of August 9, 1896 in Russia Archived August 9, 2009, at the Wayback Machine

.jpg.webp)

